A guide to Industrial Cooling Technologies
Industrial cooling solutions relate to different types of cooling used in complex environments. Cooling technologies must offer excellent performance and efficiency in a commercial or industrial setting.
Managing excess heat generated by system processes is difficult. Larger facilities may choose industrial cooling towers for their higher capacity and energy efficiency. Other operations wishing to avoid open-circuit cooling towers may choose adiabatic systems, which require a smaller installation footprint and less industrial water to function.
The most common industries using industrial cooling are data centres, manufacturing, petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals. These have sizable, ongoing cooling requirements, and operational costs must be considered. Precise temperature control is often required, especially during increased demand. Therefore, choosing the right industrial cooling system is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Below is a guide to industrial cooling technologies. We hope you find it useful.
1. Understanding industrial cooling
Definition and significance:
Managing heat is the primary requirement of industrial cooling systems. Whatever type of heat reduction methodologies are employed, cooling processes are designed to capture heat, process, and remove it.
Important systems will fail to operate optimally without adequate heat removal and cooling. Many will eventually break down due to overheating, excessive part wear, and other factors. A lack of heat mitigation could become a serious safety concern if unmanaged.
The situation becomes acute in hotter and/or more humid environments. Nevertheless, even in colder locations, heat must be removed from HVAC systems, air compressors, server rooms, factory equipment, and elsewhere.
Applications:
Manufacturing plants rely on consistent, stable processes to deliver predictable outcomes. This is true whether the plant manufactures food, industrial machinery, or OEM replacement parts.
Maintaining cool temperatures is equally important for data centres. Server rooms are packed with racks and racks of computer servers, hard drive storage bays, and network switches, and heat levels rise rapidly and precipitously if cooling suddenly stops. For this reason, backup generators or other redundancies are used to manage downtime and allow for maintenance work.
Food production facilities and related food storage also require temperatures within a tight range. Otherwise, quality preservation is at risk, and food could go bad before its best-before date.
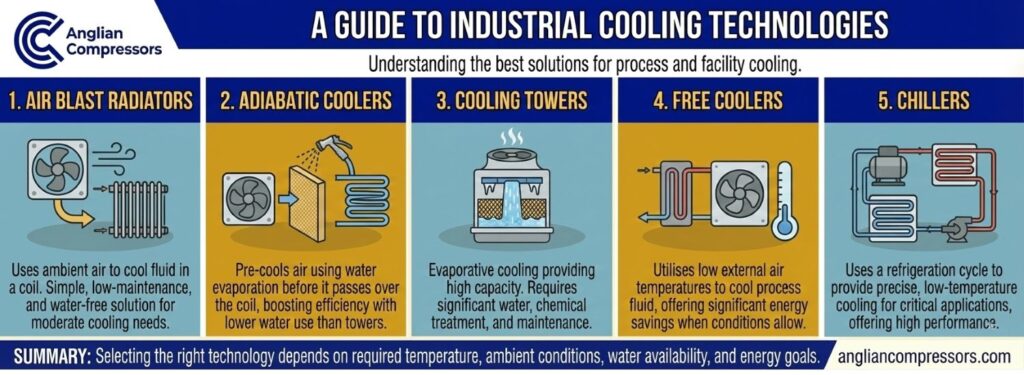
2. Types of industrial cooling technologies
There are different types of industrial process cooling systems. Below, we explain each of them.
Air cooling systems
Air-cooled systems rely on ambient air rather than water as their primary heat removal method. Ambient air is used to dissipate heat. Outdoor installations are common for these types of cooling systems. Water access, supply, and costs are not deciding factors.
While these systems are practical for medium or smaller loads, they are not ideal in all situations. For the system to function as intended, the ambient temperature must be cool or temperate, and humidity levels must remain low.
Liquid cooling systems
Liquid cooling often uses chillers in an industrial setting. Water is used to absorb heat, and this is more efficient than water-cooled systems. Sometimes, glycol is used as a heat-absorbing liquid solution.
Either a refrigeration absorption or vapour compression cycle is used. These units function especially well at power plants, where extreme heat levels exist and consistent, high performance is required.
The downsides include the need for continual water availability and a water treatment facility. Maintenance is also more demanding, including preserving industrial pumps and pipework.
Evaporative cooling systems
Evaporative cooling relies on water evaporation to lower temperature levels. Tall water cooling towers commonly use this process. These systems perform best in low-humidity environments. Access to easily accessible, continually flowing, and affordable water is essential.
While evaporation is energy-efficient, water supply expenditures balance out the cost savings. Evaporative cooling methods are often best for high cooling loads and applications where temperatures must remain consistently within a tight range.
Frequent maintenance is necessary to remove scale and address microbial issues. This prevents health risks associated with water-based systems, such as Legionella. Risk assessment and monitoring are required under the UK’s Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 and the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002.
Adiabatic cooling systems
Adiabatic cooling systems remove heat using both water and air. A heat exchanger transports ambient air across hot water-filled pipework, reducing temperature levels. The basic idea is similar to how car radiators operate, but adiabatic cooling equipment is more modular in design, making it easier and less costly to install.
These systems, which run as dry coolers during moderate seasons, only use water when ambient air is warmer and requires cooling. They find a sensible balance between being environmentally friendly and achieving better water and energy efficiency.
Let Anglian Compressors, a Branch of Atlas Copco Compressors, help you to choose the most appropriate cooling solution for your needs.

3. Selecting the right cooling system for your industry
When selecting cooling systems, match the equipment to your specific needs.
What to Consider
Heat Output: measure how much heat your machines generate. A medium-sized plastic moulding shop typically produces 150–200kW of heat that needs removing. Do not guess this figure.
Energy Use: cooling accounts for about 30% of energy costs in most factories. A Suffolk print works cut this to 19% by replacing their 15-year-old system with a standard modern one.
Weather Conditions: east Anglian humidity affects evaporative cooling. Systems that worked perfectly during installation in April often struggle in August. Check performance across all seasons.
Water Supply: some systems use surprising amounts of water. A Cambridge electronics firm pays £4,300 yearly for water for their cooling towers. Consider this ongoing cost.
Space Available: measure your available area carefully. Allow room for maintenance access – our engineers need at least 80 cm clearance around units. One Peterborough site had to remove a wall to service their poorly positioned chiller.
Regulations: water systems need regular testing under ACOP L8 guidelines. Budget about £600 annually for this testing.
Industry Examples
Manufacturing: most local factories use open cooling towers. They are effective but need monthly cleaning.
Data Centres: computer rooms often use chilled water systems. They cost more initially but use less electricity over time.
Food Production: a Thetford bakery uses closed-loop cooling with food-grade additives. More expensive but eliminates contamination risks.
Chemical Plants: tend to use traditional shell-and-tube systems. They are bulky but tolerate dirty environments well.
4. Maintenance and best practices
Regular servicing keeps cooling systems working properly. Without basic maintenance, running costs increase and breakdowns become more likely.
Why It Matters
A maintained system uses less electricity and lasts longer. We found this at a Kings Lynn warehouse, where monthly cleaning saved them £2,140 on electricity last year. Poorly maintained water systems also pose health risks through bacterial growth.
What To Do
Regular Checks: look for water leaks and rust spots monthly. It takes about 15 minutes. Water-based systems need testing under HSE’s L8 guidelines – typically quarterly for most sites.
Clean Components: air filters need washing or replacing when visibly dirty. A Wisbech printing firm cleans theirs every Monday morning before production starts. Cooling fins collect dust and need brushing or compressed air cleaning every six months.
Fluid Management: test glycol mixture strength yearly. Too weak and it freezes; too strong wastes money. The proper mix costs about £3.50 per litre, and most small systems need 20–30 litres.
Temperature Monitoring: check outlet temperatures weekly with a standard thermometer. Write them in a logbook. Most systems should run at 10–15°C. One Norfolk food processor uses a £34 wall-mounted digital thermometer with a high/low alarm.
Paperwork: keep a maintenance book near the system. A simple A4 hardback notebook works well. Note down dates, work done, and who did it.
Most mechanical issues start small. A rattling fan or valve can be fixed for under £100, but, if left unchecked, it might damage the compressor (£1,800+ to replace). Monthly checks often save thousands in repairs.
5. Innovations and future trends in industrial cooling
Emerging technologies:
AI innovations are being incorporated into new cooling systems. This includes real-time optimisations, smart reminders, and prompts based on sensory feedback and interpretation.
Power cooling systems are beginning to support renewable energy integration to reduce the environmental impact of energy consumption.
Sustainability trends:
Evaporative cooling systems are reducing their water dependence. These water-saving methodologies lower their operating expenses, reducing the total cost of ownership.
Refrigerants are transitioning to eco-friendly alternatives. These support a lower global warming potential versus previous refrigerants used.
Conclusion
Industrial cooling systems provide heat mitigation and removal for commercial and industrial operations. Maintaining cooler temperatures allows equipment to operate more efficiently. This supports existing capital investment, making systems more sustainable while reducing potential breakdowns.
Anglian Compressors, a Branch of Atlas Copco Compressors, are experts in cooling technologies. Why not arrange a consultation to discuss the creation of a tailored solution? Contact us today to see how we can help your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best cooling system for limited space?
For tight spaces, consider closed-loop dry coolers or compact chillers. A bakery in Bury St Edmunds installed a vertical dry cooler that took up just 2 square metres of yard space. These units initially cost about 20% more but fit where traditional cooling towers will not. Microchannel condensers also work well in cramped areas.
How often should cooling systems be serviced?
Most systems need quarterly checks at a minimum. Water systems require more frequent attention – typically monthly cleaning and water testing. A plastic moulding factory in Thetford schedules basic maintenance every six weeks, which takes our engineers about 90 minutes. They have not had an emergency call-out in three years. Cooling towers need more frequent cleaning, especially during pollen season when filters clog faster.
Can cooling systems use less water?
Yes. Modern systems use significantly less water than older ones. Hybrid dry coolers only use water during hot days, saving thousands of litres. A Cambridge brewery replaced its open cooling tower with a closed-loop system last summer, cutting its water usage by 83%. The payback period was 14 months based on water savings alone. Even simple measures like fixing leaky valves make a difference – one dripping valve wastes about 5 litres daily.

